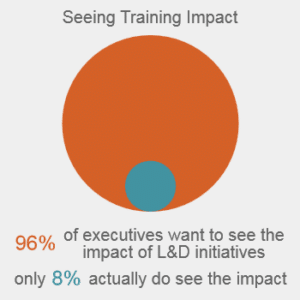
Back in 2010, Jack and Patti Phillips asked CEOs how they measure learning success. Their top answer: business impact. How successful are L&D organizations at proving business impact? Not very, according to the Phillips. Only 8% of the executives they interviewed said they see the impact of their L&D initiatives, but 96% want to see it.
 The situation hasn’t changed much since then. Business executives surveyed by Personnel Today ranked career development as a top outcome of training initiatives, but not business impact. In a 2015 poll, ATD found that alignment of learning with business goals was one of the top 3 issues faced by learning organizations.
The situation hasn’t changed much since then. Business executives surveyed by Personnel Today ranked career development as a top outcome of training initiatives, but not business impact. In a 2015 poll, ATD found that alignment of learning with business goals was one of the top 3 issues faced by learning organizations.
L&D’s challenge in showing its value with specific, measureable results has bigger consequences. It means that L&D organizations are viewed as reactive, tactical order takers. In fact, according to Bersin, one-fifth of organizations are in that category and fewer than 50% feel they are perceived by their stakeholder leadership as strategic partners.
What are some of the results of this perception?
- Budget cuts: When times are tough, L&D budgets are some of the first to be cut because there’s a perception that training doesn’t deliver results. It’s not that training doesn’t deliver. It’s that L&D doesn’t make the connection.
- Fire-drill approach: Because L&D leaders aren’t valued as strategic partners, they aren’t involved in the organization’s strategic planning. This means many business units turn to L&D as a last resort (when the fire is already burning) to fix urgent problems. It’s not that training isn’t successful. It’s that L&D is so busy putting out fires that it doesn’t have the opportunity to measure and document successes.
- Under-used training: Even in good times, L&D organizations have difficulty attracting enthusiastic learners. According to GoodPractice, two of the biggest challenges facing L&D in 2016 are learner apathy and lack of time for learning. It’s not that training isn’t effective. It’s that L&D hasn’t shown its value.
How can starting with the end in mind help change these perceptions?
- Be good at business.
To adapt a quote from Jay Baer, “The goal isn’t to be good at training. The goal is to be good at business because of the training. Measuring training comes down to how well it achieves business goals.”
 During the planning stage of every new training initiative, be sure you understand fully the business goals driving the project. Answer these questions: How will this project add value to the company? What money will the company make because of this training? Ask your business stakeholders for their answers, too.
During the planning stage of every new training initiative, be sure you understand fully the business goals driving the project. Answer these questions: How will this project add value to the company? What money will the company make because of this training? Ask your business stakeholders for their answers, too.
For example, if a business unit asks for sales training for account managers, ask questions that allow you to identify the underlying business driver. Is the problem that your account managers are recruited directly from college and lack the business acumen to interact with the C-suite teams who buy your products? Or is it that your company has a new product offering and your sales team doesn’t understand how to differentiate it from your competitors’ offerings? Use a technique such as the 5 Whys to get to the root cause of the problem.
Often training is only one component of a strategic solution such as a new product launch. For a successful launch, the product marketing team will use a full court press that includes marketing, development teams, and more. Align with them on the outcome and uncover the components that require training.
- How much revenue do they expect the new product to generate?
- How does the product fit within your company’s strategic objectives?
- What metrics would constitute success?
- What percent of the success will L&D contribute?
- What is the project’s value to the organization?
Get specific. Ask for numbers. Be sure to identify and review all measurements the training solution might impact, effects on other areas, etc. Then, working backward like a CSI expert from bone fragments to a complete person, design a robust training program with those metrics as outcomes.
But tracking to business outcomes isn’t the only solution. It’s time to include new metrics in the mix. And that’s where marketing comes in.
- Choose the right metrics for your business.
L&D’s challenge to provide effective metrics doesn’t seem to be a problem of awareness. Kirkpatrick’s 5 levels easily roll off L&D professionals’ tongues, and, as the Phillips point out, ROI certification is now offered globally.
The problem seems to be that we aren’t measuring what matters.
 According to marketing metrics gurus like Rebecca Lieb, the most important metric is the one that matters most to your business. As Lieb says, “It makes no difference whatsoever what MY most important content marketing metric is – the real question is: what metric, what key performance indicator is most important to your business? No two marketers’ objectives are exactly alike. What matters is aligning against business goals, not all the abstract things you can measure.”
According to marketing metrics gurus like Rebecca Lieb, the most important metric is the one that matters most to your business. As Lieb says, “It makes no difference whatsoever what MY most important content marketing metric is – the real question is: what metric, what key performance indicator is most important to your business? No two marketers’ objectives are exactly alike. What matters is aligning against business goals, not all the abstract things you can measure.”
Lieb’s point applies equally well to L&D. Unfortunately, many L&D professionals focus only on Kirkpatrick Levels 1 and 2—consumption and learner perceptions—metrics senior executives find irrelevant. No measurement framework will be useful unless it ties explicitly with business goals and KPIs. Every time.
For example, how can consumption metrics (think Kirkpatrick’s Level 1) be reframed to connect with business goals? Consumption metrics are often the easiest for L&D professionals to gather. They chart the number of people who have viewed, downloaded, completed, or listened to a training program. To make them more valuable, don’t stop at just the total numbers; instead, look for trends in the data.
- How is the audience interacting with the training and for how long?
- How much time are they spending on individual pages?
- Do patterns vary by learner group?
- Do you see any patterns between training consumption and business performance?
Do these trends and patterns offer ideas for segmenting the training so it more closely meets learner needs? Do people consuming this training engage in other more desirable behaviors relevant to your business goals? The bottom-line is this: choose your metrics wisely, then go deep, surfacing connections with business outcomes and KPIs.
There’s one final consideration before you begin your project. Learners.
- Redefine your learners as customers.
Take a lesson from marketing and see your audience not just as learners, but also as customers.
View training as an opportunity not just to teach, but also to buy new, loyal customers.
 According to Keith Gibson’s blog at elearningindustry.com, “If we treat our learners as potential customers who have to be sold on the value of a product, we are more likely to produce training that actually gets through and changes behavior.”
According to Keith Gibson’s blog at elearningindustry.com, “If we treat our learners as potential customers who have to be sold on the value of a product, we are more likely to produce training that actually gets through and changes behavior.”
Think of every training project like a marketing campaign using these 3 steps.
- Awareness: What type of training methods can you use to increase awareness of the project before it even begins, i.e., to bring learners into the funnel?
- Interest/Evaluation: After they’re in the funnel, how can you increase their enthusiasm about the project and prove your solution will be beneficial to them?
- Commitment/Repeat: How can you increase learners’ commitment to the L&D organization and their willingness to return for future training and recommend training solutions to their peers?
This shift also changes the types of metrics that will be valuable for explaining L&D’s success. For example, how do successful and enthusiastic learners/customers impact your company’s bottom line by increasing brand awareness and loyalty, improving employee retention and your ability to attract new talent?
By starting with the end in mind, you’ve created a solid foundation for training success. But before you dive wholeheartedly into design and development, we recommend an additional step: a thorough understanding of your audience. You’ve started this analysis already by redefining your learners as customers. Next you’ll need to know how to ensure training changes learners’ behaviors and minds.
Subscribe
Related Articles
EPISODE 5: GOOD TRAINING BUILDS BRAND CREDIBILITY
In this conversation, Ron Zamir and John Nelson discuss the [...]
EPISODE 4: SUCCESSFULLY NAVIGATING CHANGE
< Podcast Homepage Change can be anything. That’s part of [...]
Inspire Fresh Starts with Your Onboarding Learner Journey
It turns out that a great time to make a [...]


